JST New Product Complex | Under design

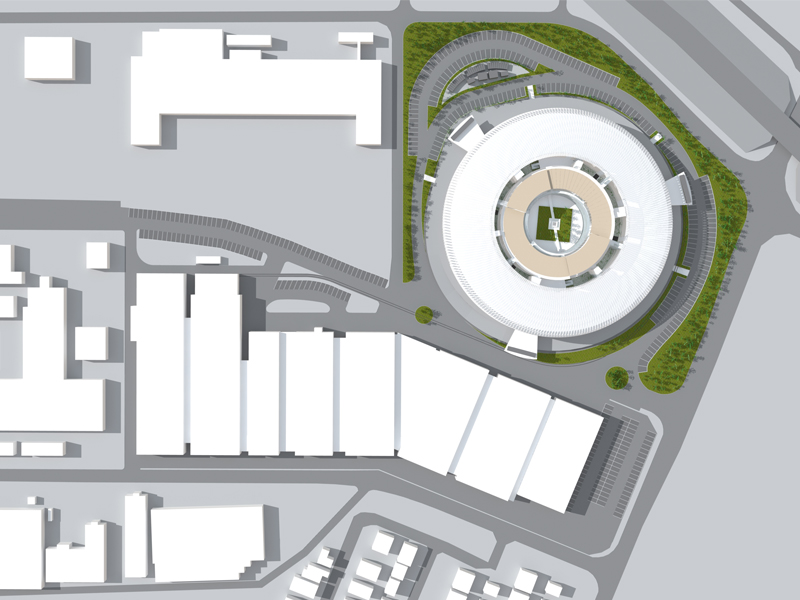
Site Location: Nishikurayoshi Land area: 58820m2 Building Use: Factory and Research Structure: Concrete and Steel Floor Area: 38866m2
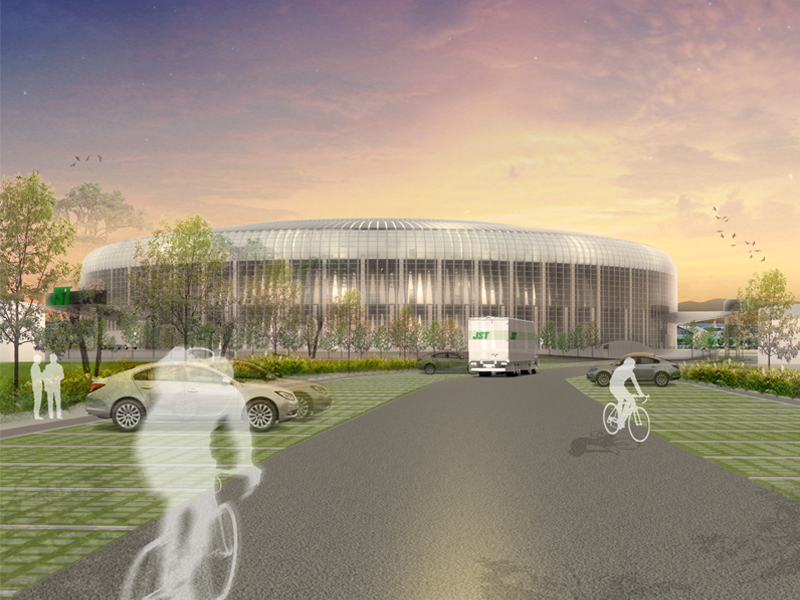
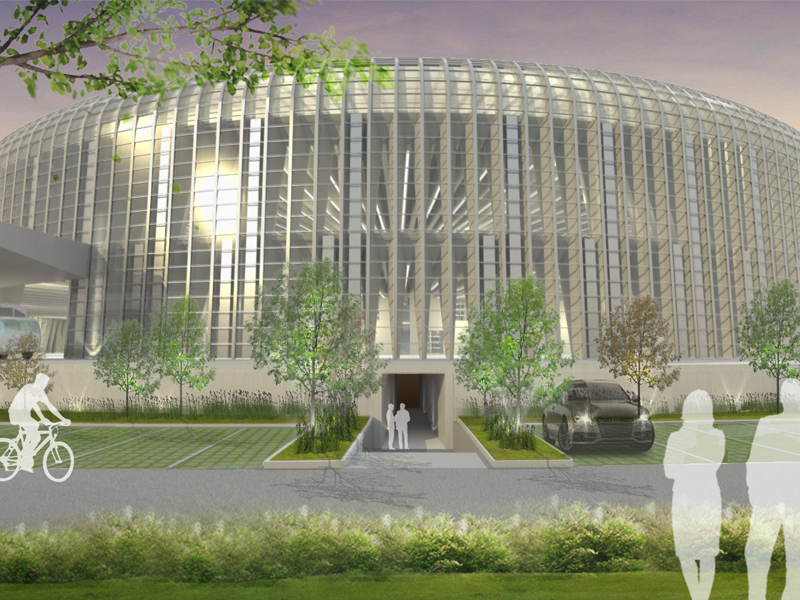
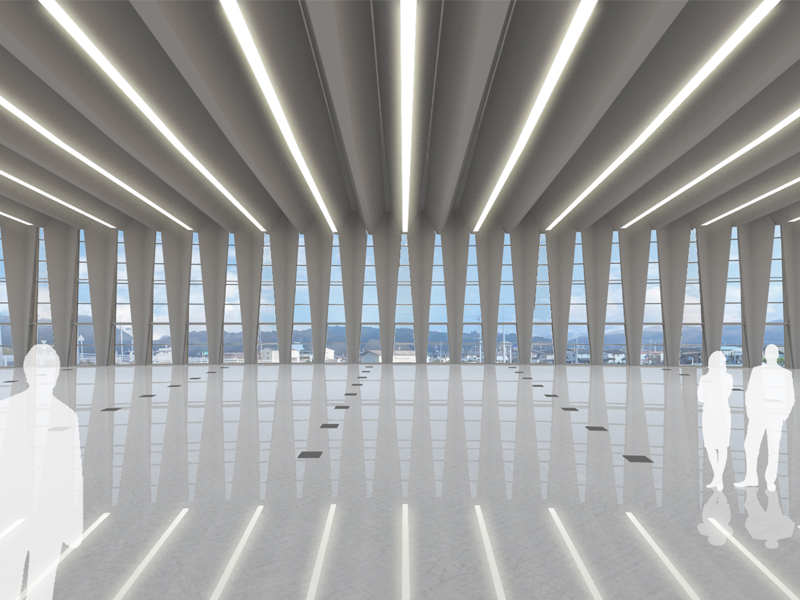
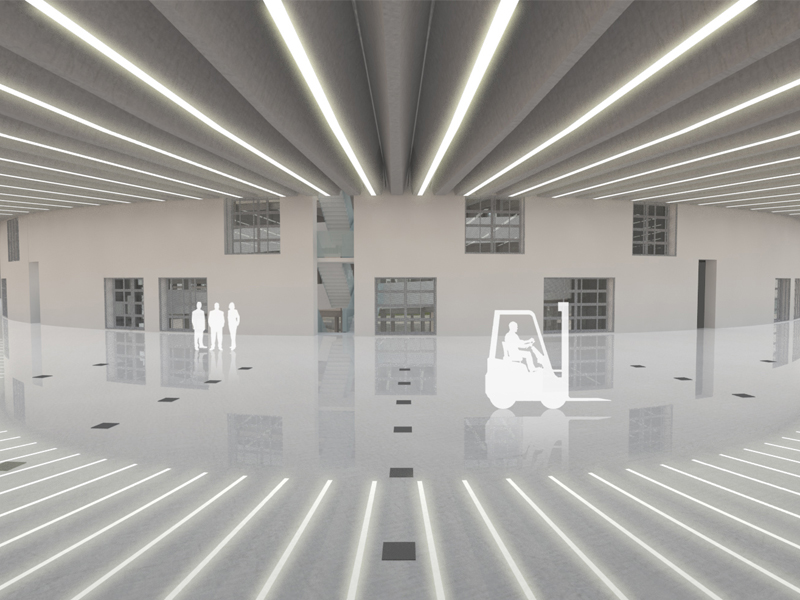
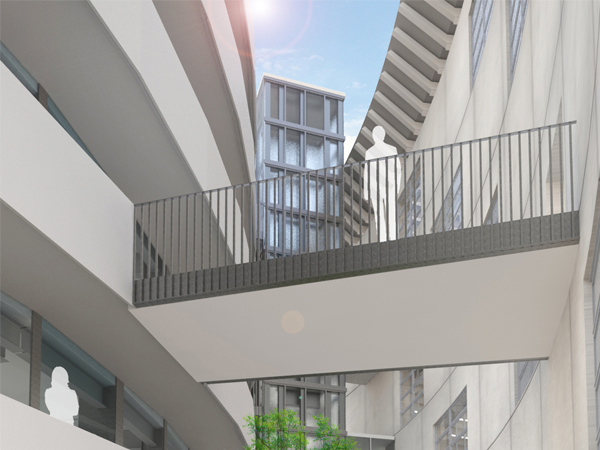
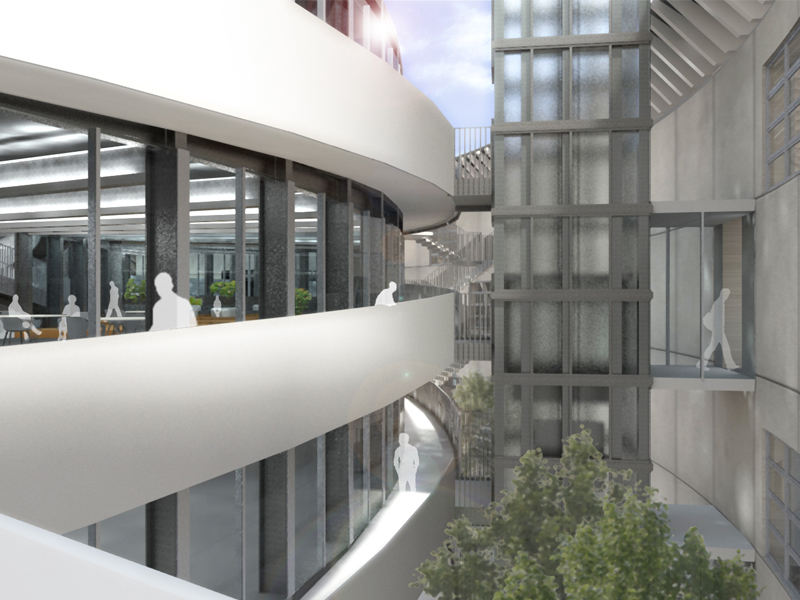
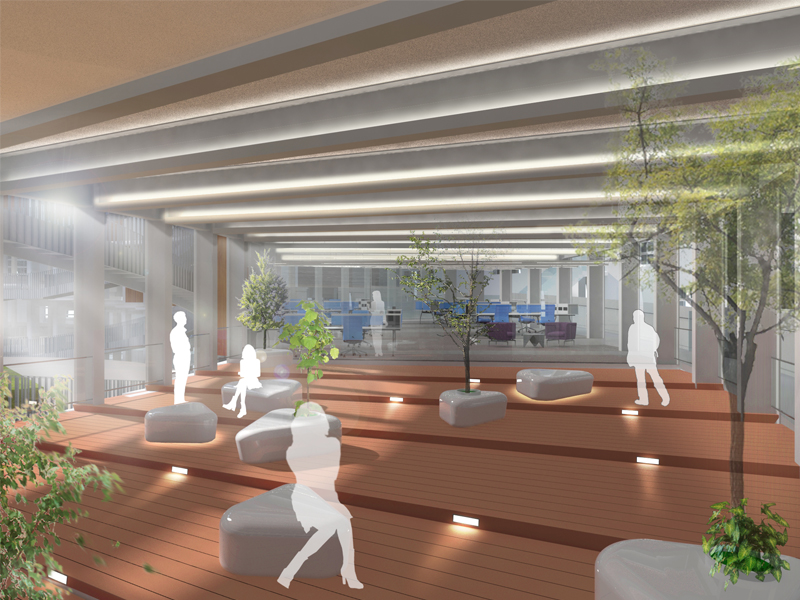
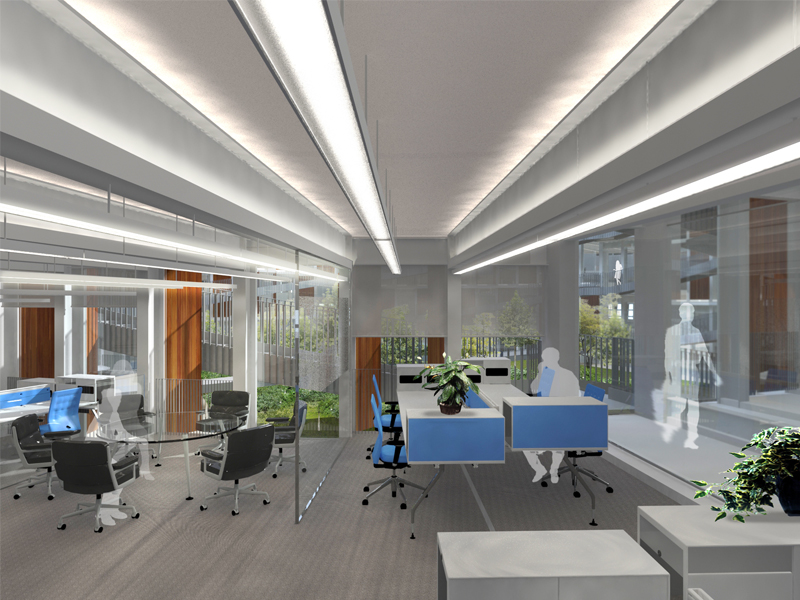
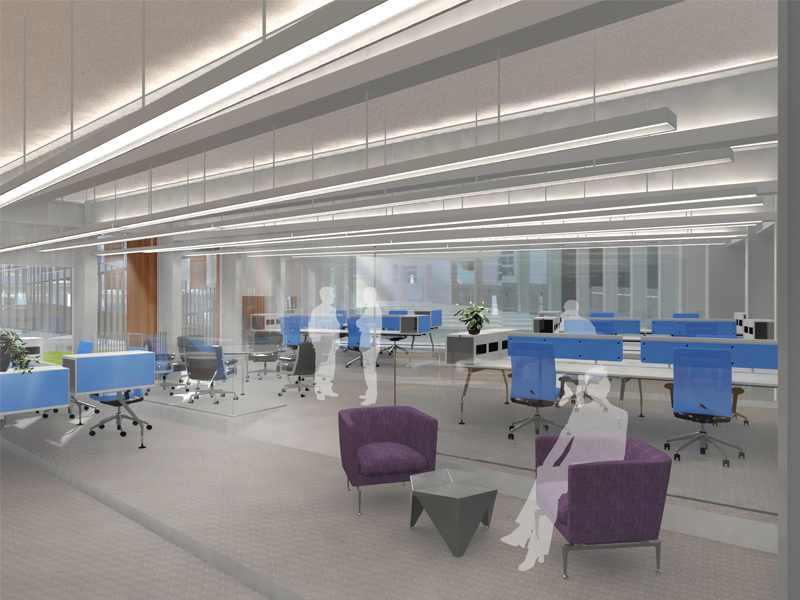
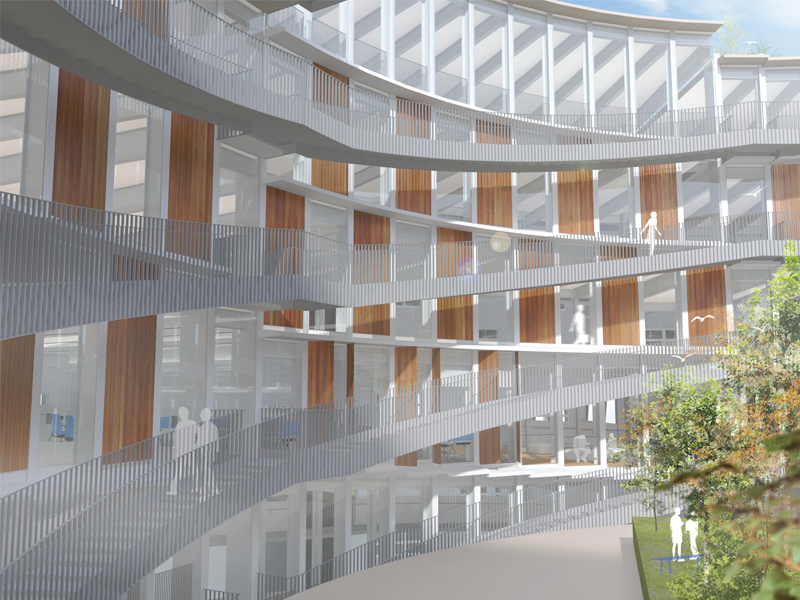
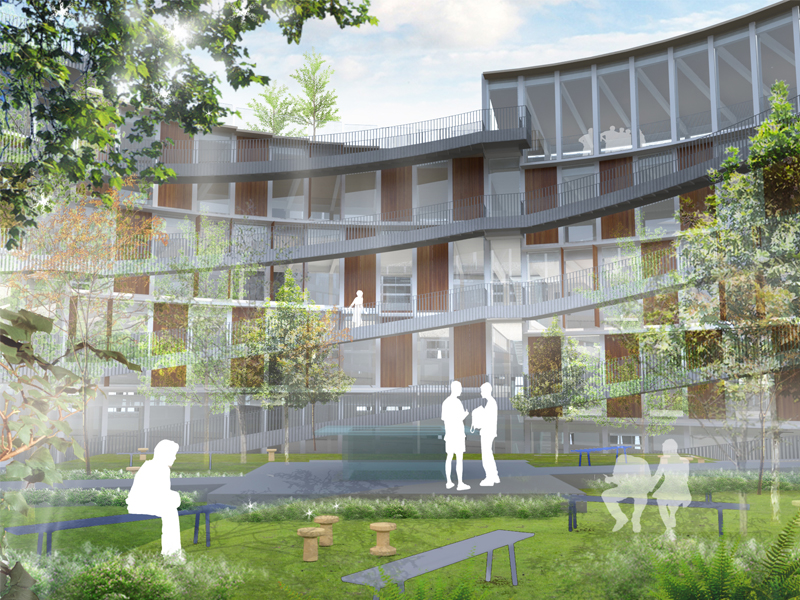
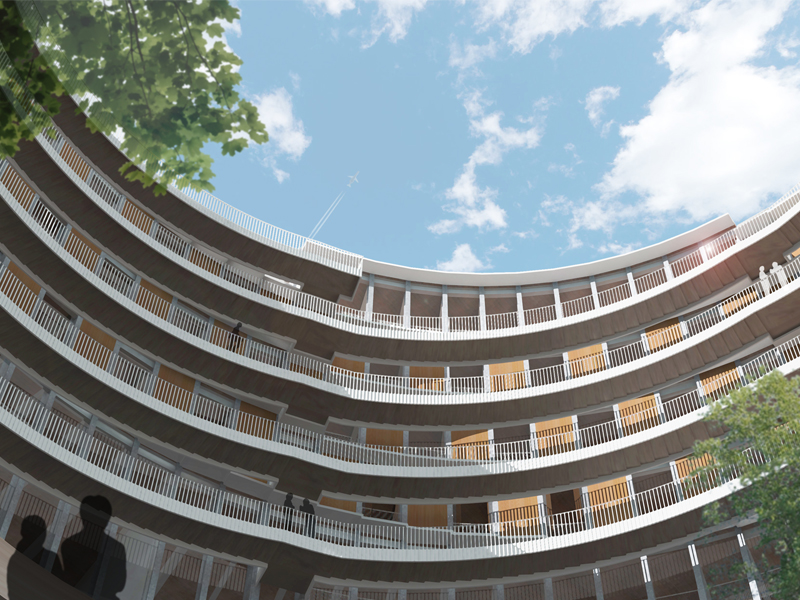
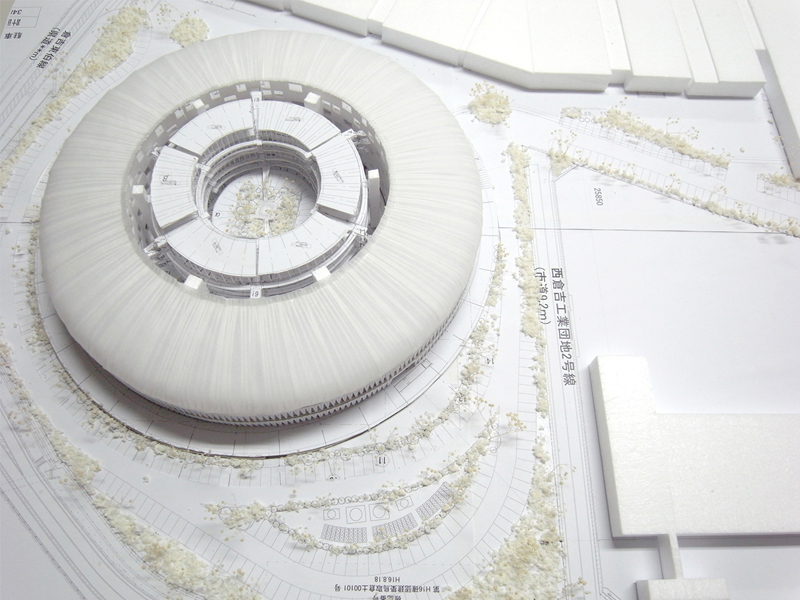
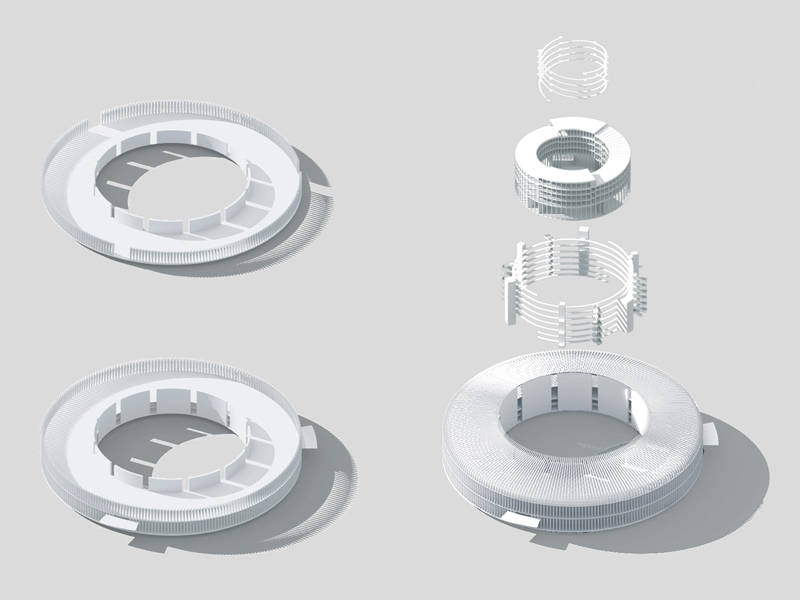
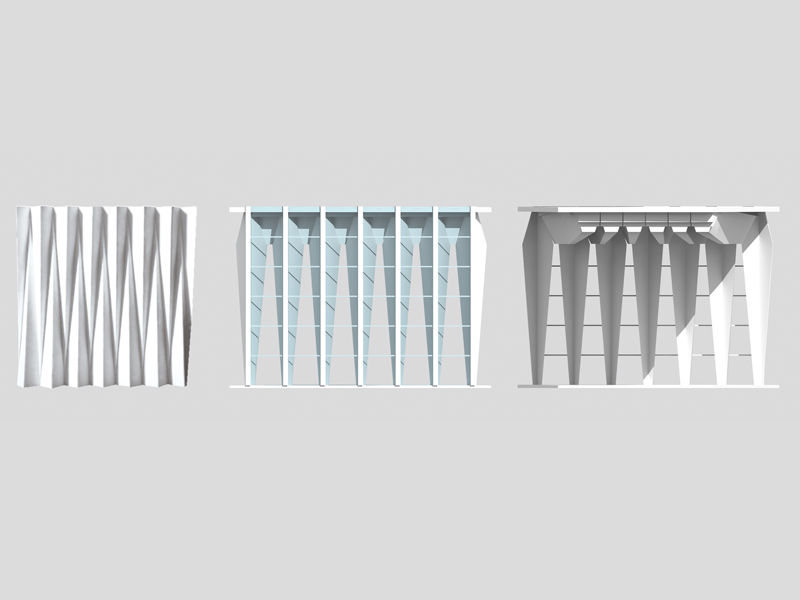
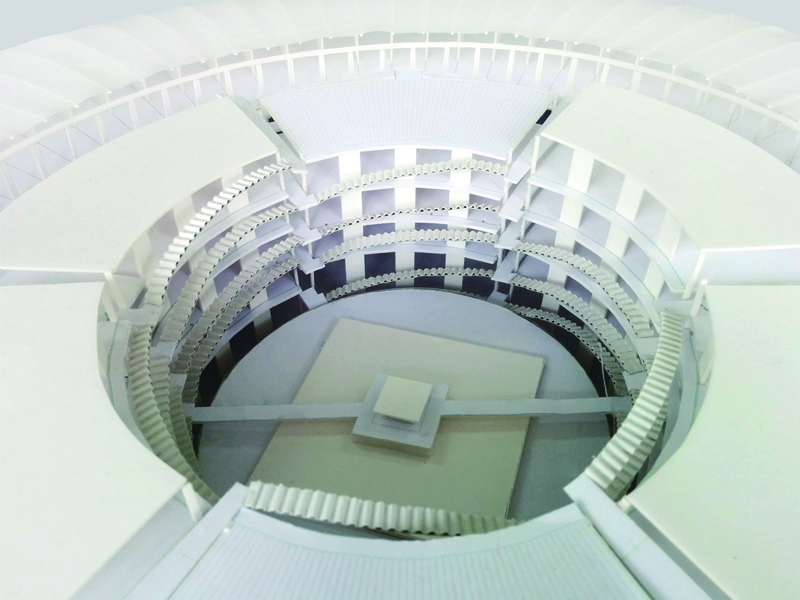
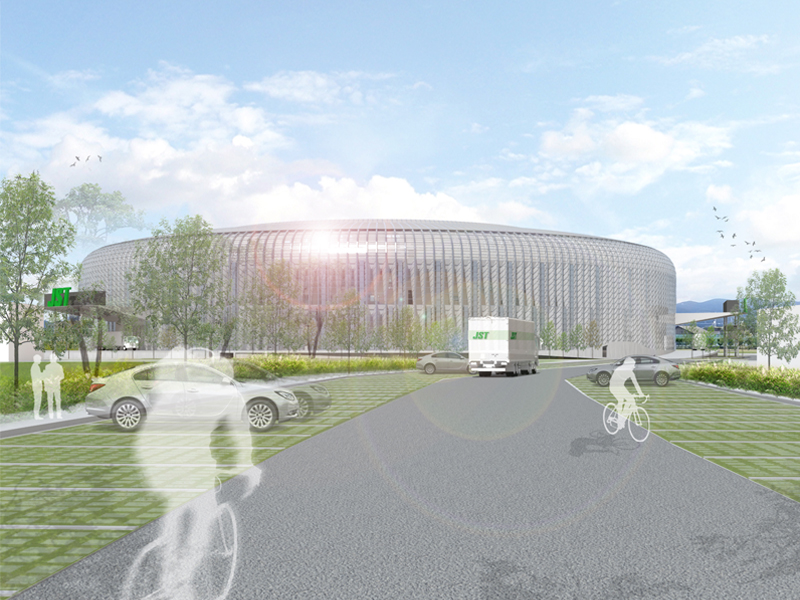
JST Nishikurayoshi is a research and production complex to develop and produce small electronic connectors for machines and computers. This building is a new addition to the existing factory complex on the same site. In general, factories just focus on the production efficiency. However, the complex aims to be an inspiring place for creation, a suitable facility for both arduous research and productive brainstorming as well. Needless to say, the design goal also includes to optimize the flow of products and to be sustainable. Since the products require flowing simply, the production process is along simple spiral lines. Spatial flexibility is very important in industrial facilities; therefore, an infinite circular loop is adopted and any kind of flow will work efficiently, no matter how long it is. The inner activities are organized into circular architectural entities: the outer ring for the production process, the innerring for the research and development of innovative products, and the Research & Development Core Room right in the center of the complex. In this area, JST will develop the machines which make their products. The green belt and the courtyard, the voids with greenery between and in the center of the 2 main rings, are working as the lungs. Concerning the flows going through the complex, the flow is divided into 2 groups: the flow of product and the flow of people. The flow of products consists of carrying in raw materials, conveying parts in the complex, and carrying out products. It is continuously supplied by external sources which orbit around the complex: trucks to/from the outside of the site, and a delivery train connected with the existing facilities on the site. The flow will start in the shipping area by unloading raw materials, and then those materials will be processed floor by floor. Once completed, the products are sent back to the shipping area and loaded on trucks. This vertical flow is operated by elevators and lifts. The horizontal flows are provided by conveys, picking robots and ceiling cranes. In contrast to the flow of products, the flow of people is free both vertically and horizontally within the entire complex. The slopes and stairs in the green belt and the courtyard allow a smooth and continuous circulation in the complex. The green belt and the inner courtyard will be very important places where people will enjoy unexpected encounters with colleagues while they are moving or having a break near greenery. It will be good opportunities to share their knowledge or ideas. Building a sustainable facility is a fundamental requirement. Therefore, sustainable methods are applied as much as possible; for example, prefabricated structure units, and passive and semi-passive ventilation and air conditioning systems. The main structure is based on the use of a few prefabricated elements. Using prefabrication allows reducing significantly energy consumption, labor, construction period, and noise and dust on the site. The structural units are designed to integrate air conditioning, plumbing, and electric lines. Moreover, they are durable to support the heavy load of the industrial machinery. The complex collects the rainwater from the roof through a gutter, and stocks it into reservoirs under the trucks’ pathway around the complex. This rainwater will be reused and sprayed in the green belt to cool the air as needed. The outer facade is covered by a double-skin. This passive system creates a draft effect and brings fresh air from the green belt and the courtyard to the outer ring through underground pipes and chambers.